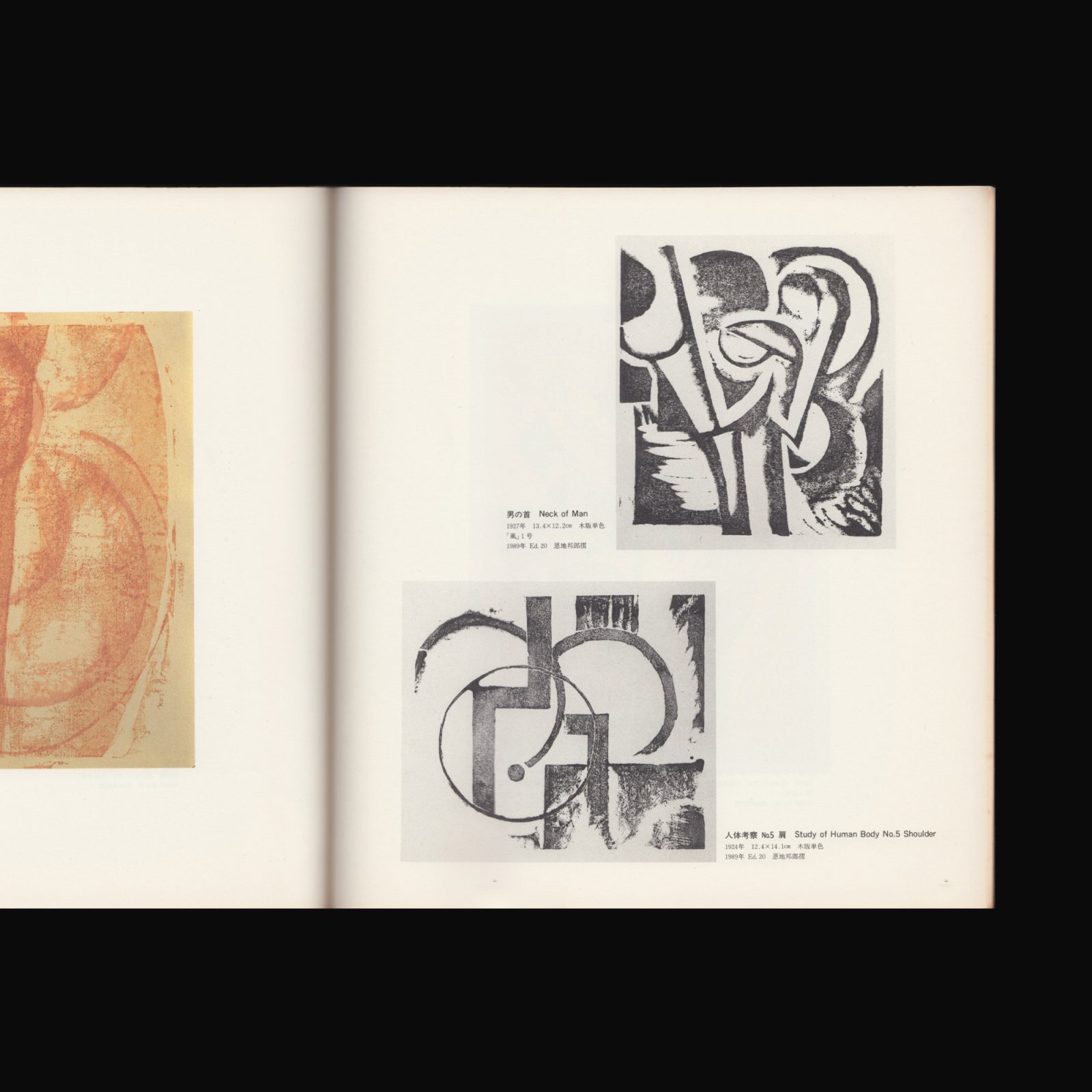
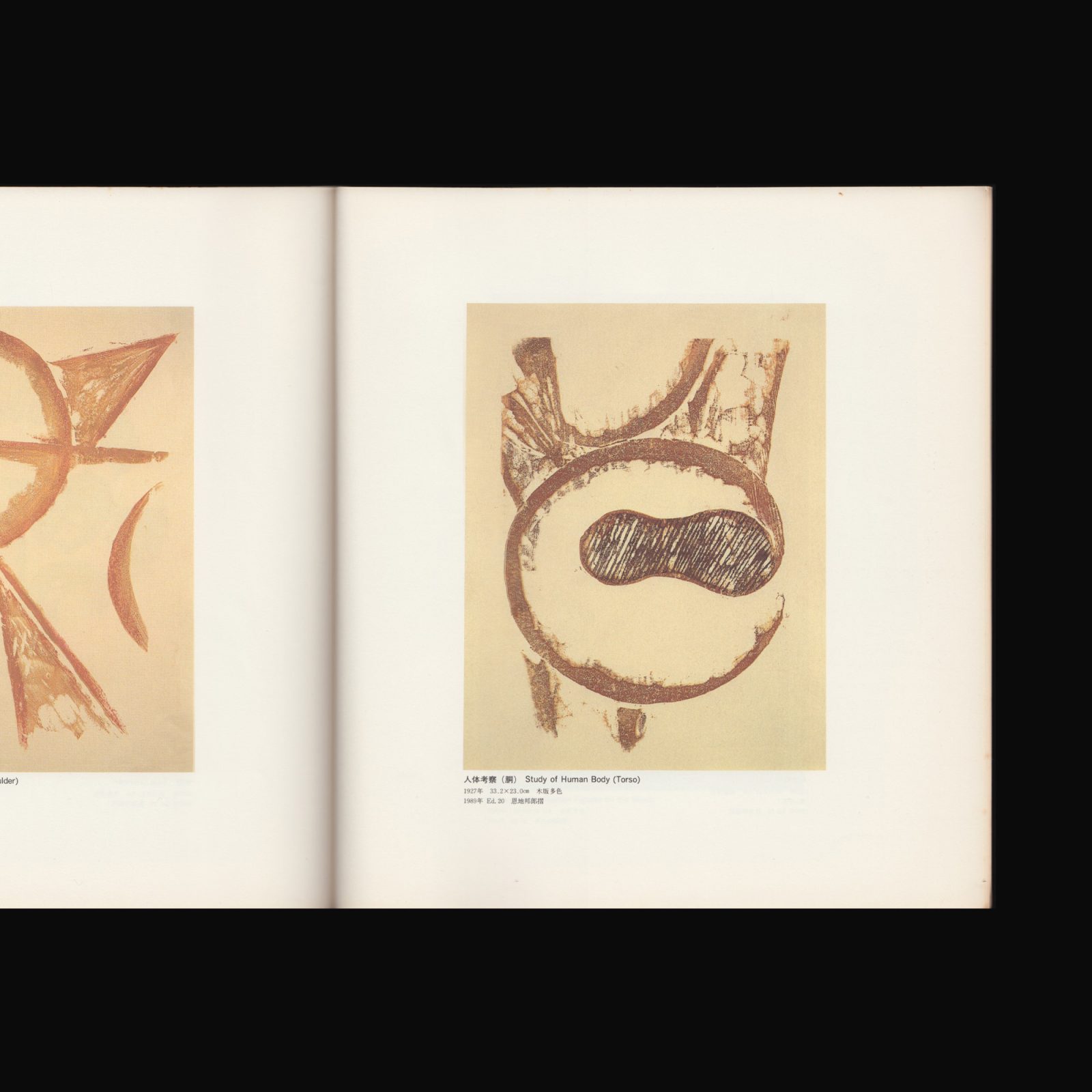
Koshiro Onchi was the most important figure in the ‘Sosaku Hanga’ movement from 1918 until his death, outstanding as a print artist, photographer, book designer and active as a poet, founder and editor of magazines, an author on the subject of prints, art and literature, a leader and organiser of societies and encourager of other artists.
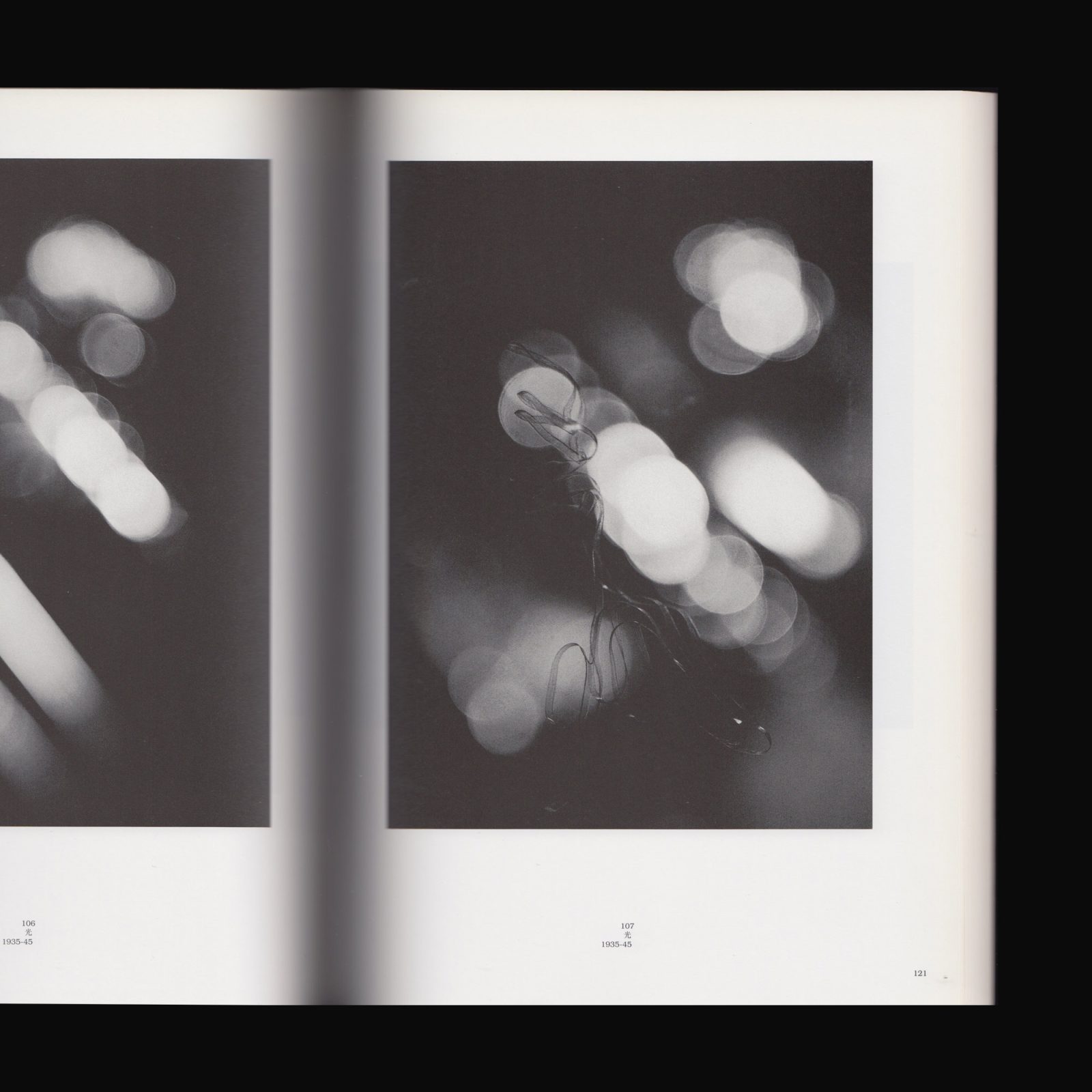








Iwata Nakayama (1895-1949) is regarded as a one of the most important contributors to the Shinko Shashin movement. After graduating from the Tokyo School of Fine Arts in 1918, he received a scholarship from the Japanese government and went to California before settling in New York. At the same time Nakayama was attracted to avant-garde movements and moved in bohemian circles where he met Shimizu Toshi. Shimizu encouraged him to move to Paris in 1926 where he met Man Ray, Fujita Tsuguji, and Enrico Prompolini. These encounters left a deep impression on him and when he returned to Japan in 1927 he energetically set about forming his own vision of ‘pure art photography’. In 1929 he settled in Ashiya (nr. Kobe) and in the following year founded the Ashiya Camera Club with Hanaya Kambei, Korai Seiji, and others. This club became the main driving force of New Photography in Japan. Together with Kimura and Nojima he founded Koga magazine in 1932 that was the most important forum for artistic photography at the time.







Produced on occasion of the exhibition From Nirvana to Catastrophe: Matsuzawa Yutaka and his ‘Commune in Imaginary Space’ at Ota Fine Arts, Tokyo, 3 March–22 April, 2017.
Yutaka Matsuzawa (1922–2006) was considered the father of Japanese conceptual art. In his pursuit of ways to express the invisible invisibly, Matsuzawa developed a unique understanding of conceptual art that both elevated and transcended the typical notions of conceptual art in the western, euro-centric art worlds.
The exhibition focused on the period 1969–1973, the most active years of Matsuzawa’s activities, and reflected on the exhibition Nirvana (1970), which was a pioneering international exhibition on Conceptualism in Japan.






The reprint of two out-of-print artist’s books self-published in the 80’s by the Japanese artists collective The Play, with a previously unreleased documentation.
Staging most of their actions, “without particular reason,” in “natural outdoor spaces,” and admitting they “only like[d] the infinite time and space of open air,” The Play is a fluctuating art collective gathering individuals with various personalities and skills, formed in 1967 in the Japanese Kansai region. Still active today the group has constantly devised its own methods for collective actions and the ways for transmitting them, its members coming together to create the possibility of an event without any concern for its result. Its persistence and longevity have set The Play apart from other groups in Japanese art history, never completely integrated, yet never completely at the margins. Refusing to distinguish art from life, The Play underlines an attitude and an outlook focused on playing, sincerity and humour, notions that remain crucial today.
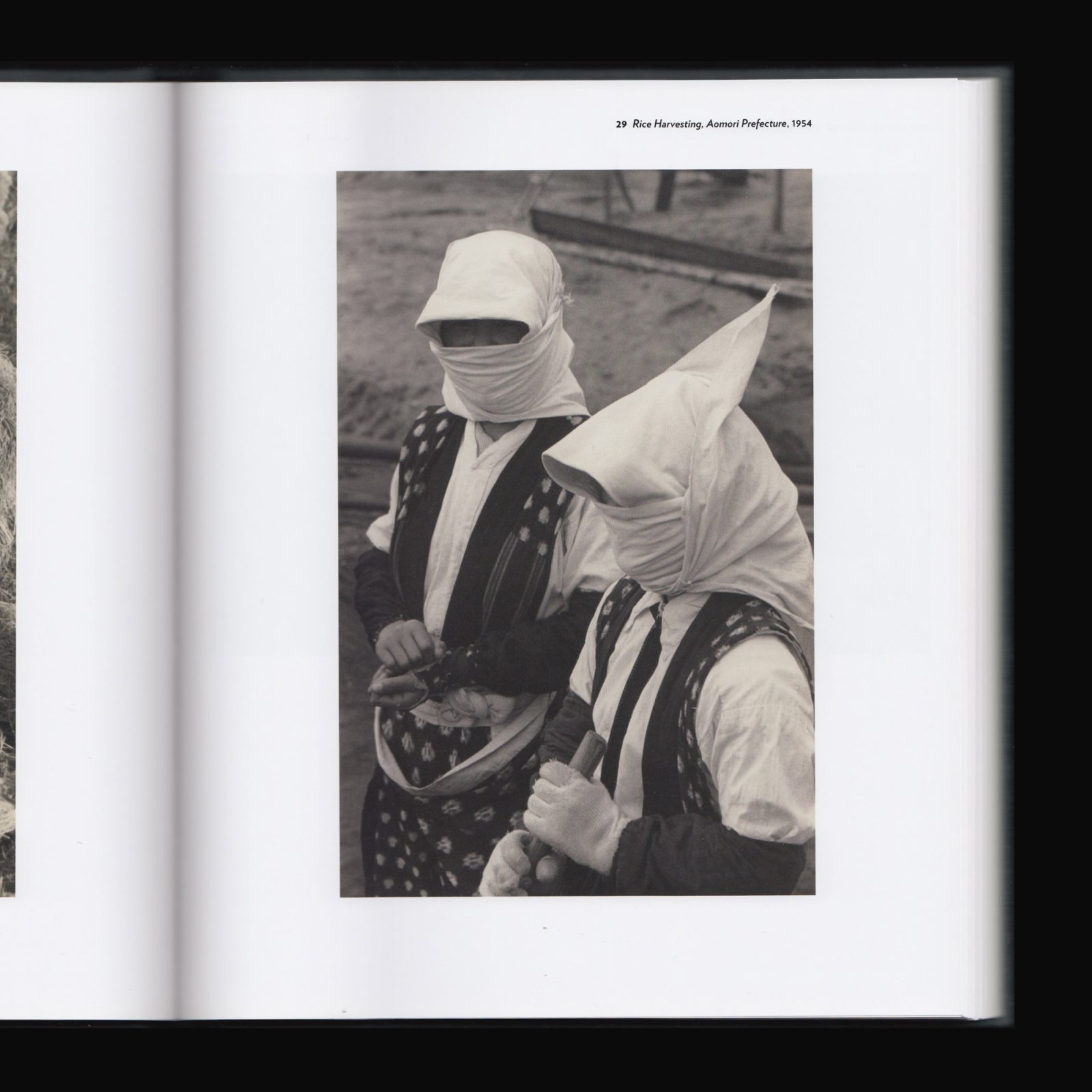






Produced on the occasion of Japan’s Modern Divide: The Photographs of Hiroshi Hamaya and Kansuke Yamamoto at the Getty Center, Los Angeles, 26 March–25 August, 2013.
Throughout his career Hiroshi Hamaya pursued objective documentation, while Kansuke Yamamoto favoured avant-garde forms of expression. These photographers embody two sides of modern Japanese life: the traditional and the forward looking, the rural and the urban, the Eastern and the Western.
Both artists grew up during the brief Taishō era (1912–1926), a period of industrialization and experimentation that ushered in the modern Shōwa era (1926–1989). It was during this time, between the international Depression and World War II, that Hamaya began to document regional traditions and social issues, primarily on the country’s rugged “back coast” along the Sea of Japan. In contrast, Yamamoto found inspiration in Surrealist art from Europe and produced innovative, socially conscious photographs, poems, and other works that advanced the avant-garde movement in Japan.








Produced on the occasion of The Art of Connecting: Atsuko Tanaka at Ikon Gallery, Birmingham, which illustrated an unprecedented balance between all aspects of Tanaka’s practice, ranging from her earliest gestures, including documentation of Gutai performances in the 1950s, to paintings made shortly before her death in 2005.
Through variety it conveys a remarkable consistency of vision, connecting art and everyday life as we know it. It articulates an artistic proposition that makes Tanaka one of the most important figures of the Japanese post-war avant-garde.